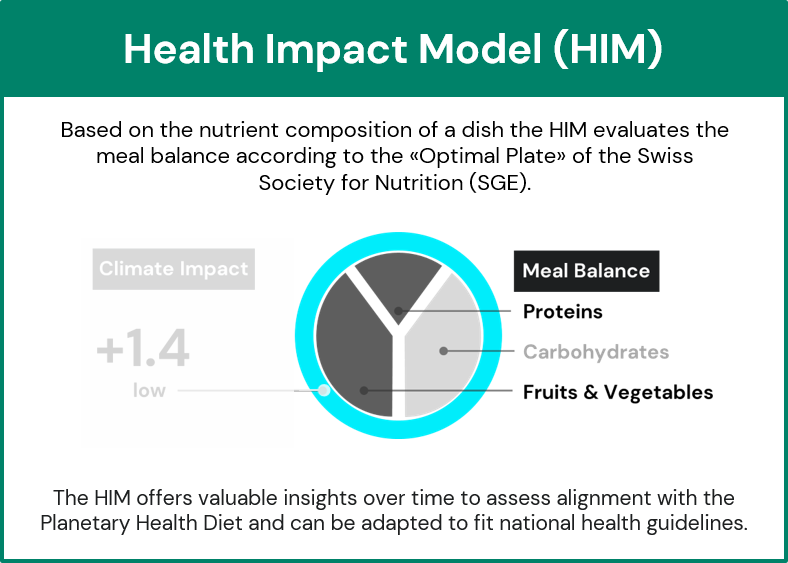
FOOD2050 simplifies complex data to help consumers and businesses align with the globally recognized Planetary Health Diet.
CIM
The CIM determines the climate impact of a company, business or individual dish in a simple degree Celsius value. Based on life cycle assessments of foodstuffs, we calculate the CO2e emissions of recipes or consumer behaviour of certain target groups and translate these into global warming potential linked to the Paris Climate Agreement.
** Paris Climate Agreement: The Paris Climate Agreement is an international treaty to limit global warming to well below 2°C, aiming for 1.5°C, by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.